- Chintamani Stainless Inc, 132, T.P. Streets, 6th Kumbharwada Lane, Mumbai- 400004, India
- Trophy Winning
- Ceritified ( ISO 9005-2010 )
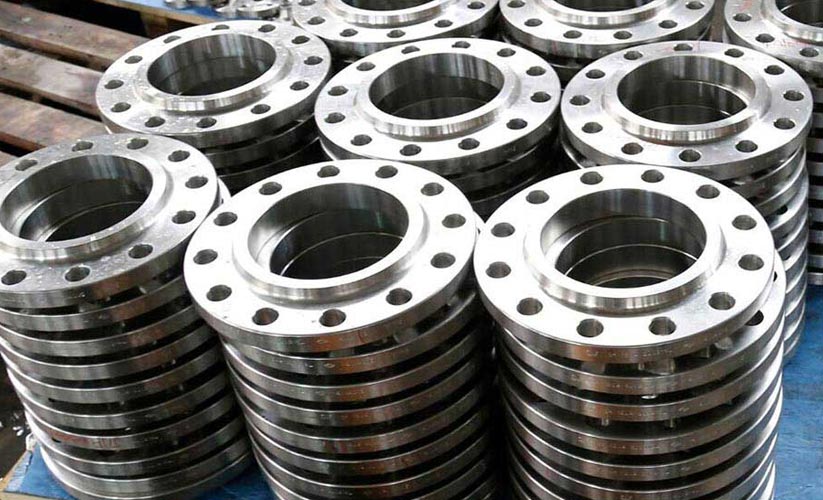
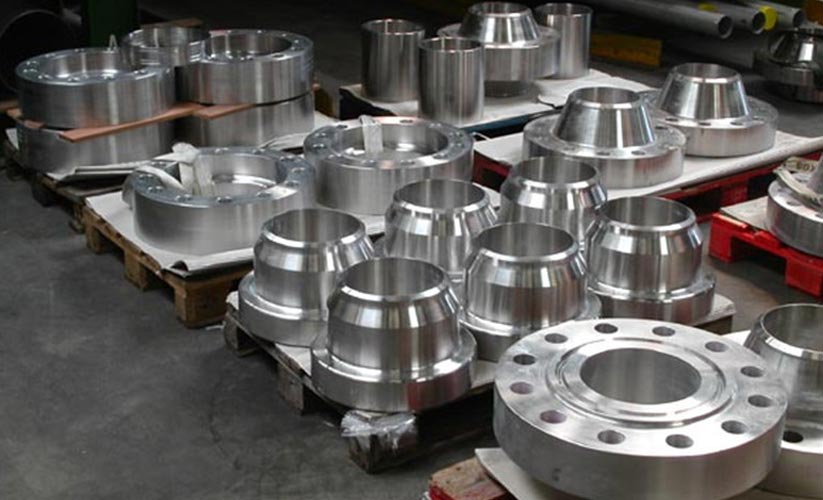
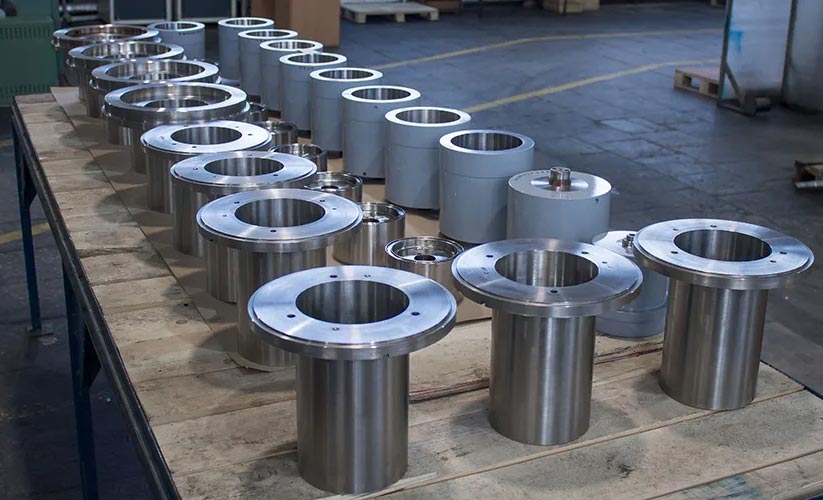
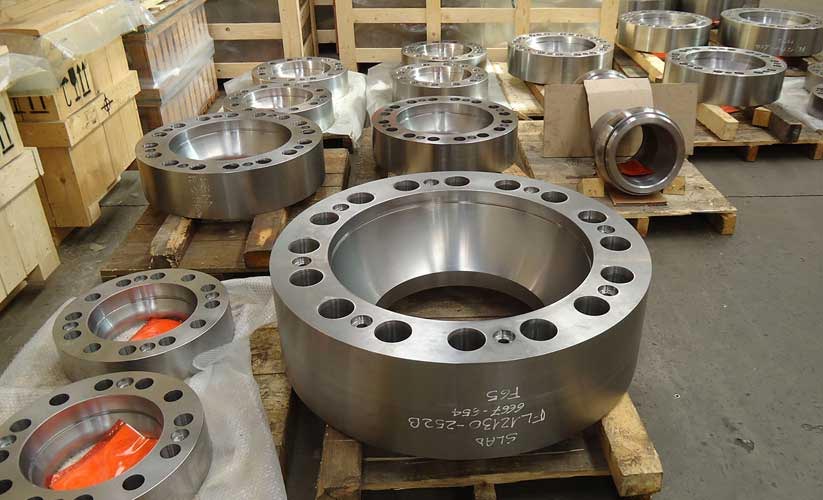




Super Duplex flanges
Chintamani Stainless Inc is ISO 9001:2008 certified manufacturer, supplier and exporter of Super Duplex Steel flanges in India and worldwide.The Super Duplex Flanges are made from super duplex steel, which has chromium, iron, and nickel in its chemical composition along with trace amounts of molybdenum. The Super Duplex Steel Flanges has both austenitic and ferritic microstructure and they have some excellent mechanical properties. The Super Duplex 2507 Flanges are known for their excellent resistance to chloride ion related stress corrosion cracking. The ASTM A182 UNS S32750 Slip On Flanges also have high thermal conductivity along with low coefficient of thermal expansion.
The chemical composition of the Din 1.4410 Pipe Flange enhances their resistance to pitting, crevice, and general corrosion. The Asme Sa182 F53 Threaded Flanges are widely used in various marine environments. The ASTM A182 UNS S32760 Blind Flanges are widely used in different piping systems to stop the flow inside. The ASTM A182 F51 Pipe Flange also has a wide range of applications in bleaching operations and selected food processing applications too. One can see the 2507 Super Duplex Welding Neck Flange is greatly used in shipbuilding companies for applications like propellers, shafts, pumps, valves, and so on. Basically, the Uns S32750 Socket Weld Flange is designed for those applications that need good corrosion resistance and enhanced strength.
The Alloy 2507 Blrf Flanges also show enhanced resistance to inorganic acids, especially
in chloride containing media. Even though the Super Duplex Steel 2507 Orifice
Flanges can be exposed to diluted hydrochloric acid containing environments, they should
not be exposed to the concentrated HCl.
The balanced dual phase microstructure in the alloy of Werkstoff No 1.4410 Super Duplex Blind Flanges in
conjunction with high tensile strength presents itself to be a cost effective and corrosion resistant
solution, particularly in high chloride environments. Most Super Duplex UNS S32750 Flanges have similar
advantages as its counterpart. For instance, super duplex alloys have a lower alloying cost, in addition
to having an increased tensile and yield strength unlike similar ferritic and austenitic grades with
equipment corrosion resistance in chlorine containing environments. In many cases, this gives the buyer
a much required respite while purchasing smaller or thinner cross sectioned Super Duplex Stainless Steel
Flanges without the need to compromise on both quality and performance.
The Din 1.4410 Lap Joint Flange has a very low carbon content and that is why there is a minimal risk of the occurrence of carbide precipitation at the grain boundaries during the process of heat treatment. The Saf 2507 Ring Type Joint Flange is a light-weighted product, whose shape, size, and dimensions can be customized as requested by the client.
| Specification : | Super Duplex Flanges |
| Coating Flange Faces : | Zinc Plated, Yellow Transparent, Anti-rust Paint, Cold and Hot Dip Galvanized, Oil Black Paint |
| Standards: | JIS Flanges, ISO Flanges, GOST Flanges, UNI Flanges, AWWA Flanges, MSS SP44 Flanges, ASME B16.38 Flanges, EN-1092 Flanges, BS10 Flanges, DIN Flanges, PN Flanges, ASME B16.5 Flanges, ASME B16.47 (Series A, Series B) |
| Pressure Rating Table: | Class 150 LBS, Class 300 LBS, Class 600 LBS, Class 900 LBS, Class 1500 LBS, Class 2500 LBS |
| Common Types of Flange : | Flanges 150 LB WNRF Class 300 RTJ 600# BLRF Class 900 SORF |
| Size Chart : | 1/2″ (15 NB) To 48″ (1200NB) |
| Production Process: | Heat Treated, Machined, Forged |
| Supporting Flange Material: | Gasket, Flange Bolts, Ring Joint |
| Application: | Water Pipeline Industry Natural Gas Industry Fabrication Industry Nuclear Power Plant Chemical Industry Oil And Gas Industry |
| Design For Size: | ANSI, EN, ASA, ASME, BS, DIN, JIS, PN |
| Flange Machining Equipment: | Bending machine, Pushing Machine, Sand-blasting machine, Press machine, electric bevelling machine etc |
| Connect Type: | LJF, RF, FF, LMF, SMF, RTJ |
Super Duplex Stainless Steel UNS S32750 Flange Pressure Rating
| ASME | Super Duplex Flanges Pressure Rating | ||||||
| Temperature °F | Class 150 | Class 300 | Class 400 | Class 600 | Class 900 | Class 1500 | Class 2500 |
| -20 to 100 | 275 | 720 | 960 | 1440 | 2160 | 3600 | 6000 |
| 200 | 230 | 600 | 800 | 1200 | 1800 | 3000 | 5000 |
| 300 | 205 | 540 | 720 | 1080 | 1620 | 2700 | 4500 |
| 400 | 190 | 495 | 660 | 995 | 1490 | 2485 | 4140 |
| 500 | 170 | 465 | 620 | 930 | 1395 | 2330 | 3880 |
| 600 | 140 | 435 | 580 | 875 | 1310 | 2185 | 3640 |
| 650 | 125 | 430 | 575 | 860 | 1290 | 2150 | 3580 |
| 700 | 110 | 425 | 565 | 850 | 1275 | 2125 | 3540 |
| 750 | 95 | 415 | 555 | 830 | 1245 | 2075 | 3460 |
| 800 | 80 | 405 | 540 | 805 | 1210 | 2015 | 3360 |
| 850 | 65 | 395 | 530 | 790 | 1190 | 1980 | 3300 |
| 900 | 50 | 390 | 520 | 780 | 1165 | 1945 | 3240 |
| 950 | 35 | 380 | 510 | 765 | 1145 | 1910 | 3180 |
| 1000 | 20 | 320 | 430 | 640 | 965 | 1605 | 2675 |
| 1050 | 20 | 310 | 410 | 615 | 925 | 1545 | 2570 |
| 1100 | 20 | 255 | 345 | 515 | 770 | 1285 | 2145 |
| 1150 | 20 | 200 | 265 | 400 | 595 | 995 | 1655 |
| 1200 | 20 | 155 | 205 | 310 | 465 | 770 | 1285 |
| 1250 | 20 | 115 | 150 | 225 | 340 | 565 | 945 |
| 1300 | 20 | 85 | 115 | 170 | 255 | 430 | 715 |
| 1350 | 20 | 60 | 80 | 125 | 185 | 310 | 515 |
| 1400 | 20 | 50 | 65 | 95 | 145 | 240 | 400 |
| 1450 | 15 | 35 | 45 | 70 | 105 | 170 | 285 |
| 1500 | 10 | 25 | 35 | 55 | 80 | 135 | 230 |
A182 grade F53 WNRF Flange Pressure rating
| ASME/ANSI B 16.5 | Welding Neck Flange, Socket Weld Flange, Blind (BLRF) Flange, Lap Joint Flange, Slip on Flange, Threaded Flange, Ring Type Joint Flange, High Hub Blind Flange |
| PRESSURE CLASS | 150, 300, 400, 600, 900, 1500, 2500 |
| ASME/ANSI B 16.36 | Threaded Flange, Welding Neck Flange, Slip on Flange (SORF) |
| PRESSURE CLASS | 300, 400, 600, 900, 1500, 2500 |
| ASME/ANSI B 16.47 | Weld Neck Flange, Blind Flange [Series A & B] |
| PRESSURE CLASS | 75, 150, 300, 400, 600, 900 |
| BS 4504 SEC 3.1 | Blank Flange, Hubbed Threaded Flange, Welding Neck Flange, Lapped Pipe End Flange, Plate Flange, Loose Plate Flange, Loose Plate With Weld Neck Flange, Hubbed Slip on Flange |
| PRESSURE CLASS | PN 2.5 TO PN 40 |
| BS 1560 BOSS | Blind (BLRF) Flange, Slip-On Flange, Welding Neck Flange, Socket Welding Flange, Lapped Flange, Screwed Boss Flange |
| PRESSURE CLASS | 150, 300, 400, 600, 900, 1500, 2500 |
| BS10 | Plate Slip-On Flange, Blind Flange, Welding Neck Flange, Screwed Boss Flange, Slip-On Boss Flange |
| TABLE | D, E, F, H |
| DIN FLANGE | DIN 2527, 2566, 2573, 2576, 2641, 2642, 2655, 2656, 2627, 2628, 2629, 2631, 2632, 2633, 2634, 2635, 2636, 2637, 2638, 2673 |
| PRESSURE CLASS | PN 6 TO PN 100 |
| BS 4504[PART 1] | Hubbed Slip-On, Loose Plate With Weld On Plate Collar, Welding Neck Flange, Plate Flange, Blank Flange, Hubbed Threaded |
| PRESSURE CLASS | PN 2.5 TO PN 400 |
| Standard | Class | Diameter | Bolt Circle Diameter | Number of Bolts | Bolt Size | Diameter of Bolt Hole |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AS4087 | PN14 | 95 | 67 | 4 | M12 | 14 |
| AS 2129 | Table C | 95 | 67 | 4 | 13 | 14 |
| Table D | 95 | 67 | 4 | 13 | 14 | |
| Table E | 95 | 67 | 4 | 13 | 14 | |
| Table F | 95 | 67 | 4 | 13 | 14 | |
| Table H | 114 | 83 | 4 | 16 | 17 | |
| Table J | 114 | 83 | 4 | 16 | 17 | |
| ANSI B16.5 | ANSI 150 | 89 | 60 | 4 | 13 | 16 |
| ANSI 300 | 95 | 67 | 4 | 13 | 16 | |
| ANSI 600 | 95 | 67 | 4 | 13 | 16 | |
| ANSI 900 | 121 | 83 | 4 | 19 | 22 | |
| ANSI 1500 | 121 | 83 | 4 | 19 | 22 | |
| ISO 7005 (DIN) | PN6 | 80 | 55 | 4 | M10 | 11 |
| PN10 | 95 | 65 | 4 | M12 | 14 | |
| PN16 | 95 | 65 | 4 | M12 | 14 | |
| PN20 | 90 | 60.5 | 4 | M14 | 16 | |
| PN25 | 95 | 65 | 4 | M12 | 14 | |
| PN40 | 95 | 65 | 4 | M12 | 14 |
| European Series | American Series |
|---|---|
| Type B (Raised Face) | Raised Face (RF) |
| Type A (Flat Face) | Flat Face (FF) |
| Type G (O-Ring Spigot) | Ring Joints Face (RJ) |
| Type D (Groove) | Groove (G) |
| Type C(Tongue) | Tongue (T) |
| Type F (Recess) | Male (M) |
| Type E (Spigot) | Female (F) |
| Type H (O-Ring Groove) | - |
| BS10 | Welding Neck Flange, Plate SORF Flange, Screwed Boss Flange, Slip-On Boss Flange, Blind Flange |
| TABLE | E, D,H, F |
| ASME/ANSI B 16.47 | Blind Flange [ A & B], Welding Neck Flange |
| CLASS | 400, 900, 150, 300, 75, 600 |
| ASME/ANSI B 16.5 | Threaded Flange, Slip on Flange, Blind Flange, High Hub Blind Flange, Socket Weld Flange, Welding Neck Flange, Lap Joint Flange, Ring Type Joint Flange |
| CLASS | 400, 2500, 300, 150, 1500, 900, 600, |
| SEC 3.1 BS 4504 | Loose Plate Flange, Blank Flange, WNRF Flange, Hubbed Slip on Flange, Hubbed Threaded Flange |
| CLASS | PN 2.5 - PN 40 |
| ASME/ANSI B 16.36 | WNRF Flange, Threaded Flange, SORF Flange |
| CLASS | 2500, 900, 300, 600, 1500, 400 |
| BOSS BS 1560 | Lapped Flange, WNRF Flange, SORF Flange, BLRF Flange, Socket Welding and Screwed Boss Flange, |
| CLASS | 400, 900, 600, 2500, 1500, 150, 300 |
| [PART 1] BS 4504 | Plate Flange, Welding Neck Flange, Blank Flange, Hubbed Slip-On Hubbed Threaded, |
| CLASS | PN 2.5 - PN 400 |
| FLANGES DIN | DIN 2632, 2631, 2527, 2637,2638, 2633, 2576, 2566, 2573, 2634, 2635, 2629, 2628, 2641,2642, 2636, 2656, 2673, 2627, 2655 |
| CLASS | PN 6 - PN 100 |
| Grade | Mn | C | Si | S | P | Mo | Cr | N | Ni | Fe |
| S32750 | 1.20 max | 0.030 max | 0.80 max | 0.020 max | 0.035 max | 3.00 – 5.00 | 24.00 – 26.00 | 0.24 – 0.32 | 6.00 – 8.00 | 58.095 min |
| Grades | Density (lb/in 3) | Melting Point (°F) | Melting Point (°C) | Density (g/cm 3) |
| S32750 | 0.281 | 2460 | 1350 | 7.8 |
General characteristics
Steel designations |
Performance |
Typical chemical composition, % by mass |
||||||||||
name |
EN |
ASTM |
UNS |
PRE |
A1) |
Rp0.2 |
Grade |
C |
Cr |
Ni |
Mo |
N |
| 2507 | 1.4410 | 2507 | S32750 | 43 | 20 | 550 | D | 0.02 | 25.0 | 7.0 | 4.0 | 0.27 |
| 2205 stainless steel grades | Industry Specifications | UNS |
| Duplex 2507 2507 (EN 1.4410/UNS S32750) A super duplex product with higher corrosion resistance and mechanical strength than Forta DX 2205. Often used in extremely corrosive environments. |
• Desalination plants • Industrial piping • Scrubbers • Oil and gas industry, typically tubular products, flanges,fittings and valves • Deep-sea pipelines |
• Cold rolled coil and sheet • Hot rolled coil and sheet • Quarto plate • Bar • Wire rod • Semi-finished (bloom, billet, ingot & slab) |
| Duplex 32760 100 (EN 1.4501/UNS S32760) A super duplex product with higher corrosion resistance and mechanical strength than Forta DX 2205. Often used in extremely corrosive environments. |
• Desalination plants • Industrial piping • Scrubbers • Oil and gas industry, typically tubular products, flanges, fittings and valves • Deep-sea pipelines |
• Cold rolled coil and sheet • Hot rolled coil and sheet • Quarto plate • Bar • Wire rod • Semi-finished (bloom, billet, ingot & slab) |
Performance
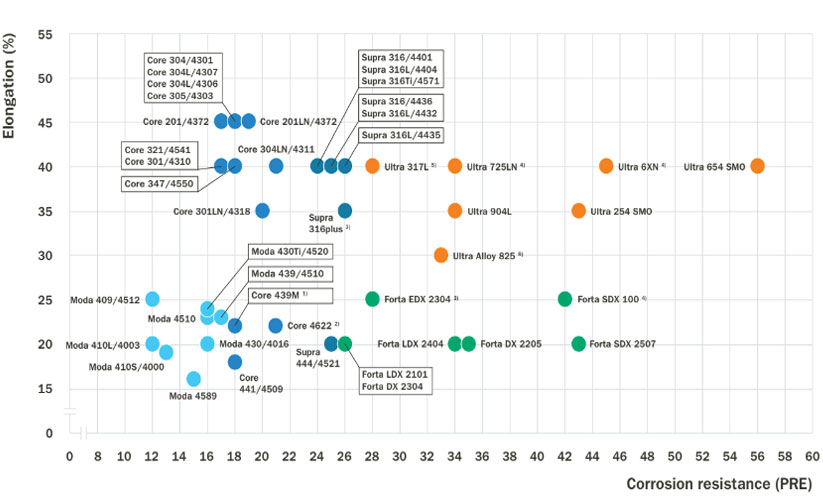
Elongation vs. corrosion resistance.
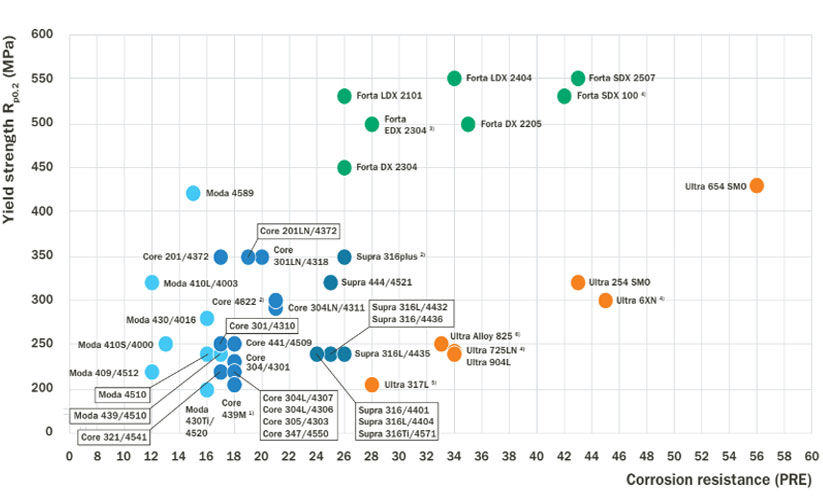
Elongation vs. Corrosion resistance
Strength vs. Corrosion resistance

Elongation vs. Corrosion resistance

Duplex stainless steels, known for their high chromium content, provide excellent corrosion resistance, particularly in uniform corrosion environments with rates below 0.1 mm/year. Forta DX 2205 shows superior resistance to chloride-contaminated sulfuric acid compared to traditional stainless steels like Supra 316L/4404, approaching the performance of Ultra 904L. In dilute hydrochloric acid, Forta SDX 2507 and similar high-alloyed duplex steels are suitable, though localized corrosion risks exist around crevices even within safe usage limits.
Corrosion resistance
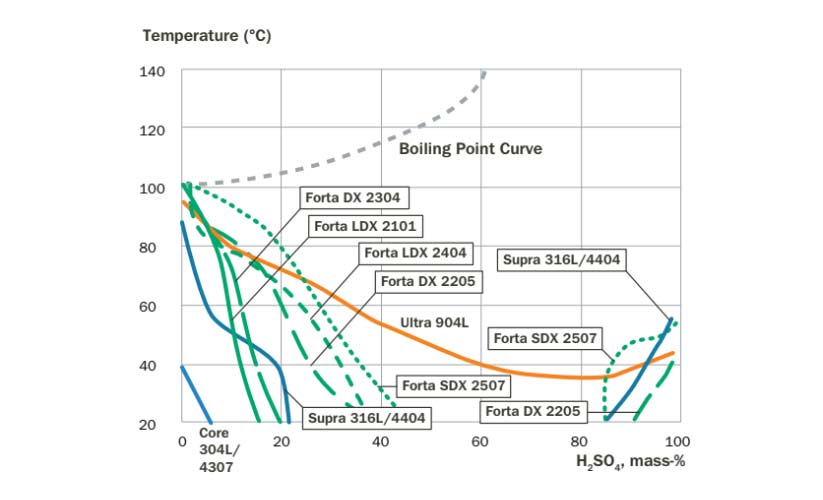
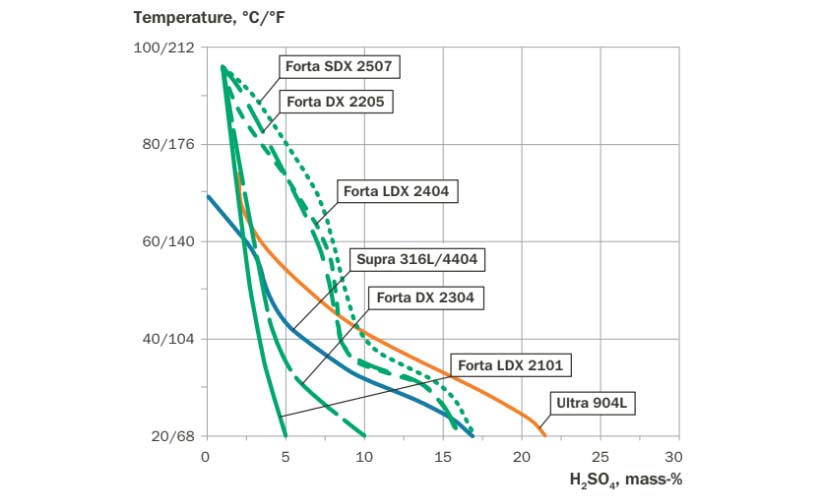
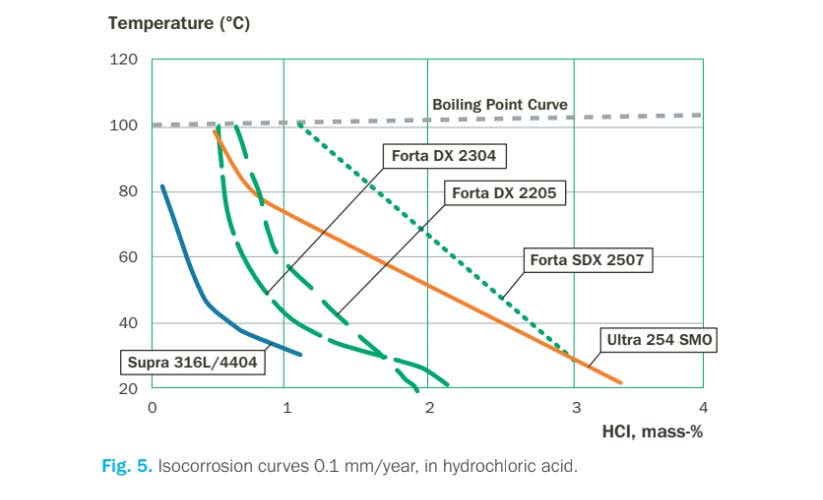
- Uniform Corrosion: Due to high chromium content, these steels resist uniform corrosion well, typically less than 0.1 mm/year.
- Sulfuric Acid: DX 2205 shows superior resistance in sulfuric acid contaminated by chloride ions compared to Supra 316L/4404.
- Hydrochloric Acid: SDX 2507 and DX 2205 can be used in dilute hydrochloric acid, with potential risks of localized corrosion in crevices.
- Nitric Acid: LDX 2101 and DX 2304, with their high chromium content and low molybdenum, are suitable for environments where resistance to strongly oxidizing nitric acid is needed.
PRE values for Forta Duplex grades and some austenitic grades
Steel designations |
PRE |
|||
| name | EN | ASTM Type |
UNS | |
| 2205 | 1.4462 | 2205 | S32205 | 35 |
| 2507 | 1.4410 | 2507 | S32750 | 43 |
Results from stress corrosion cracking immersion tests in chloride solutions
| name | ASTM G123 | ASTM G36 | ||
| 25% NaCl, pH 1.5, 106°C (b.p.), 1,000 h | 40% CaCl2, 100°C, 500 h | 45% MgCl2, 155°C (b.p.), 24 h | ||
| U-bend samples | 4-PB samples (90% of Rp0.2) | U-bend samples | ||
| 2205 | No SCC | No SCC | SCC | |
| 2507 | No SCC | No SCC | SCC | |
Mechanical properties according to EN 10088 and EN 10028
| EN | ASTM | Product form | Yield strength | Tensile | Elongation | Elongation | |
| name | UNS | Rp0.2[MPa] | strength | A[%] | A80[%] | ||
| Rm[MPa] | |||||||
| 2507 | 1.4410 | S32750 | Cold rolled coil (C) | 550 | 750–1000 | 20 | 20 |
| Hot rolled coil (H) | 530 | 750–1000 | 20 | 20 | |||
| Quarto plate (P) | 530 | 730–930 | 20 | 20 | |||
| Bar | 530 | 730–930 | 25 | – | |||
| 1.4510 | S32760 | Cold rolled coil (C) | 550 | 750–1000 | 20 | 20 | |
| Hot rolled coil (H) | 530 | 750–1000 | 25 | 25 | |||
| Quarto plate (P) | 530 | 730–930 | 25 | 25 |
Mechanical properties according to ASTM A240
| EN | ASTM | Product form | Yield | Yield | Tensile | Tensile | Elongation | |
| name | UNS | strength | strength | strength | strength | A50[%] | ||
| Rp0.2[MPa] | Rp0.2 [ksi] | Rm [MPa] | Rm [ksi] | |||||
| 2507 | 1.4410 | S32750 | Plate, sheet and strip | 550 | 80 | 795 | 116 | 15 |
| 100 | 1.4501 | S32760 | Plate, sheet and strip | 550 | 80 | 750 | 108 | 25 |
Mechanical properties at elevated temperatures, minimum yield strength according to EN 10028-7
| name | Strength | 100°C | 150°C | 200°C | 250°C | |
| 2507 | Tensile strength | Rm [MPa] | 680 | 660 | 640 | 630 |
Physical properties
Metric values according to EN 10088-1
| name | EN | ASTM Type | UNS | Density [kg/dm3] | Modulus of elasticity at 20°C [GPa] | Coefficient of thermal expansion 20–100°C [10-6/K] | Thermal conductivity at 20°C [W/(m x K)] | Thermal capacity at 20°C [J/(kg x K)] | Electrical resistivity at 20°C [Ω x mm2/m] |
| 2507 | 1.4410 | 2507 | S32750 | 7.8 | 200 | 13.0 | 15 | 500 | 0.8 |
| 100 | 1.4410 | - | S32760 | 7.8 | 200 | 13.0 | 15 | 500 | 0.8 |
Imperial values converted from Table 10
| name | Density [lbm/in3] | Modulus of elasticity [psi] | Coefficient of thermal expansion 68–212°F [μin / (in x °F)] | Thermal conductivity [Btu/(hr x ft x °F)] | Thermal capacity [Btu/(lbm x °F)] | Electrical resistivity [μΩ x in] |
| 2507 | 0.282 | 29 x 106 | 7.2 | 8.7 | 0.119 | 31.50 |
Fabrication
Duplex stainless steel is suitable for all forming processes used for stainless steel. The high yield strength compared to austenitic and ferritic stainless steel can however give differences in forming behavior. Depending on the chosen forming technique there could be consequences, such as increased springback. This point is particularly relevant to the forming of any high strength steel. Moreover, an excellent interplay between high yield strength, work hardening rate and elongation promote the duplex grades for light weight and cost-efficient applications with complex shapes. The impact of the high strength varies for different forming techniques. Common for all is that the estimated forming forces will be higher than for the corresponding austenitic and ferritic stainless steel grades. This effect will usually be lower than expected from just the increase in strength since the choice of duplex stainless steel is often associated with gauge reduction. It is important to consider that duplex stainless steel may also be more demanding on the tools and on the lubricant. This should also be noted when looking to down gauge.
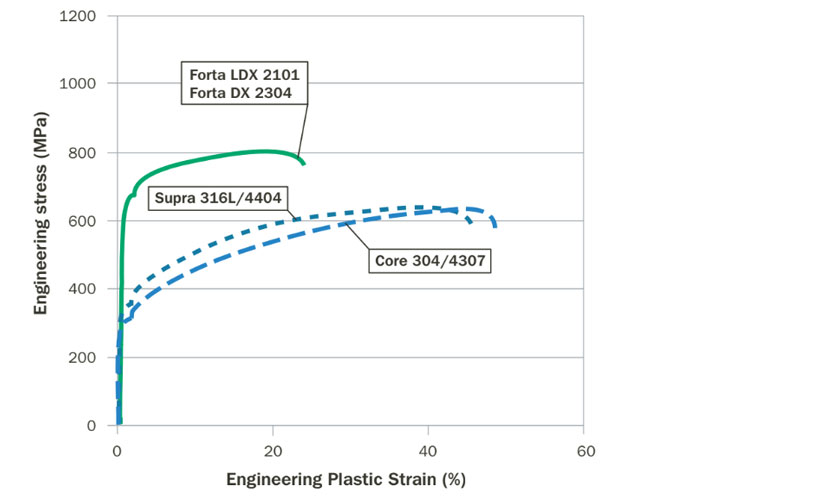
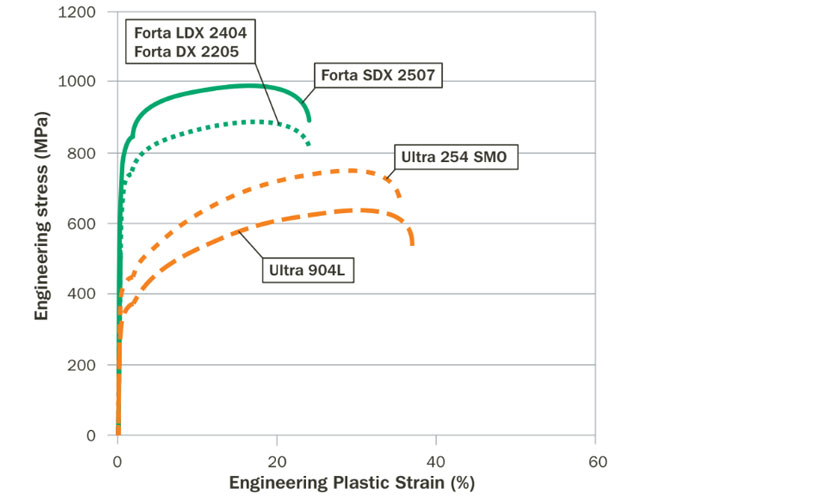
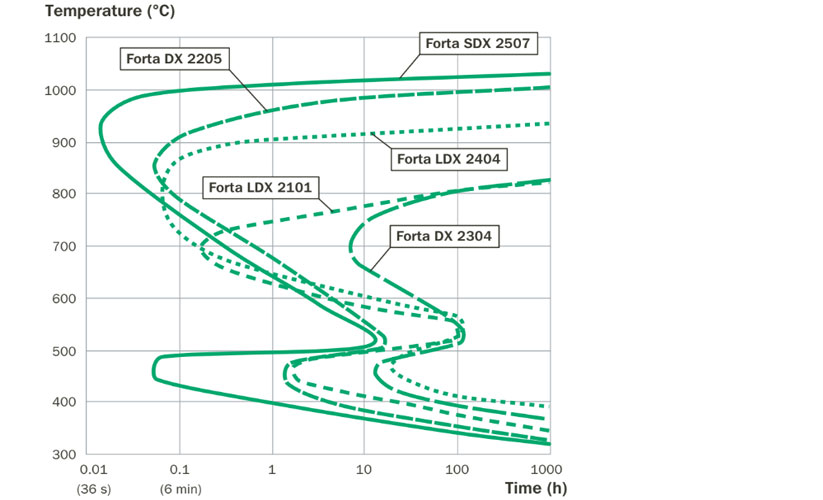
Welding consumables
| name | EN | ASTM Type | UNS | Consumable ISO designation |
| 2507 | 1.4410 | 2507 | S32750 | 25 9 4 NL |
General characteristics
Steel designations |
Performance |
Typical chemical composition, % by mass |
||||||||||
name |
EN |
ASTM |
UNS |
PRE |
A1) |
Rp0.2 |
Grade |
C |
Cr |
Ni |
Mo |
N |
| 2507 | 1.4410 | 2507 | S32750 | 43 | 20 | 550 | D | 0.02 | 25.0 | 7.0 | 4.0 | 0.27 |
Product
Quick contact
Get Solution
Organically grow the holistic world view of disruptive innovation via workplace diversity
Contact Us